for the first time, a team of scientists and researchers have achieved sustained, high-fidelity ‘quantum teleportation’ — the instant transfer of ‘qubits’, the basic unit of quantum information. the collaborative team, which includes NASA’s jet propulsion laboratory, successfully demonstrated sustained, long-distance teleportation of qubits of photons (quanta of light) with fidelity greater than 90%. the qubits were teleported 44 kilometers (27 miles) over a fiber-optic network using state-of-the-art single-photon detectors and off-the-shelf equipment.
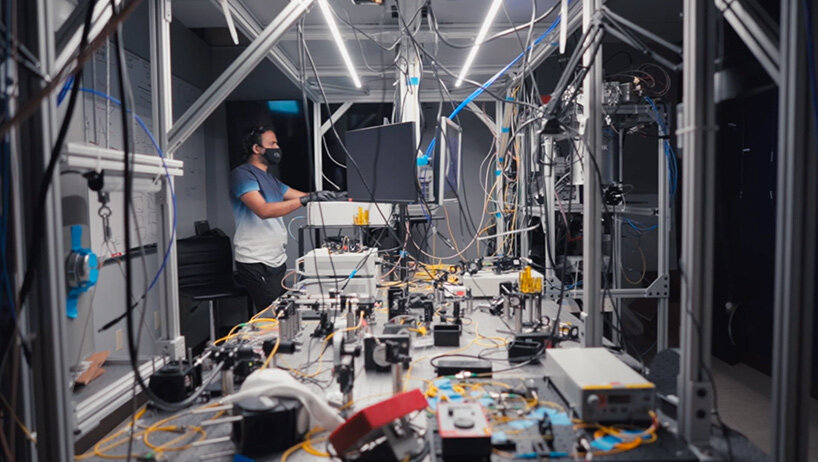

quantum teleportation is a ‘disembodied’ transfer of quantum states from one location to another. the quantum teleportation of a qubit is achieved using quantum entanglement, in which two or more particles are inextricably linked to each other. if an entangled pair of particles is shared between two separate locations, no matter the distance between them, the encoded information is teleported.
‘a viable quantum internet — a network in which information stored in qubits is shared over long distances through entanglement — would transform the fields of data storage, precision sensing and computing, ushering in a new era of communication,’ says the team behind the project, which includes researchers at fermilab, AT&T, caltech, harvard university, NASA jet propulsion laboratory, and university of calgary. a paper published in PRX quantum details the results.
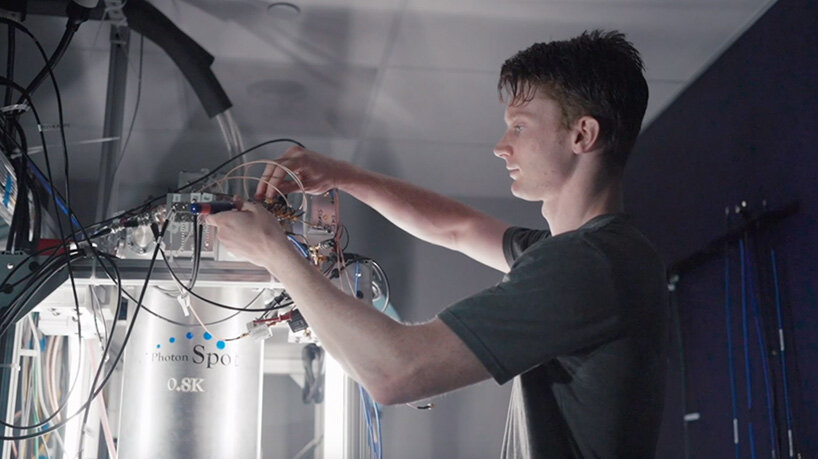

‘we’re thrilled by these results,’ says fermilab scientist panagiotis spentzouris, head of the fermilab quantum science program and one of the paper’s co-authors. ‘this is a key achievement on the way to building a technology that will redefine how we conduct global communication.’ the team successfully teleported qubits on two systems: the caltech quantum network, or CQNET, and the fermilab quantum network, or FQNET. the systems were designed, built, commissioned and deployed by caltech’s public-private research program on intelligent quantum networks and technologies, or IN-Q-NET.
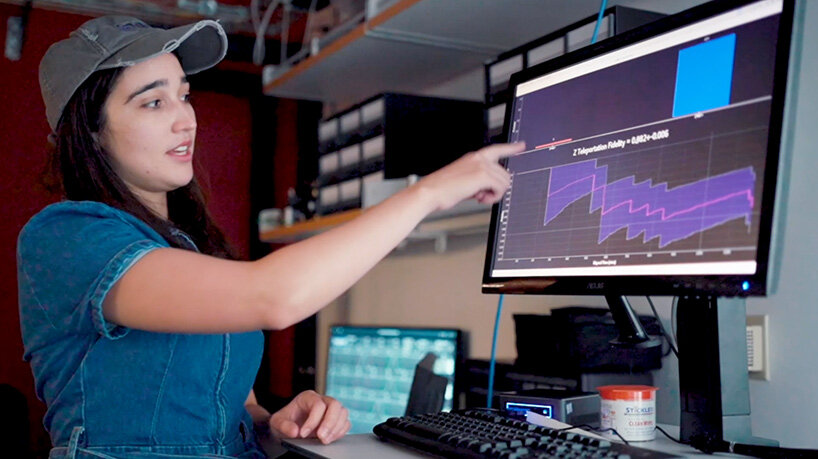

CQNET and FQNET, which feature near-autonomous data processing, are compatible both with existing telecommunication infrastructure and with emerging quantum processing and storage devices. researchers are using them to improve the fidelity and rate of entanglement distribution, with an emphasis on complex quantum communication protocols and fundamental science. the achievement comes just a few months after the U.S. department of energy unveiled its blueprint for a national quantum internet. learn more about the result here.



No comments:
Post a Comment